Difference between revisions of "Liblicense"
(→Example) |
(Libcclicense and LibccLicense merge) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[Category:Operating System]] | [[Category:Operating System]] | ||
[[Category:Technology]] | [[Category:Technology]] | ||
| + | A library for managing license metadata, in particular CC licensing information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The idea of this library started out on the [[IRC]] channel, in a discussion on how to best help boost the community of software | ||
| + | developers working with things related to CC - mostly the metadata format. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Basically, the idea is to write a portable C library that manages metadata for CC licenses, and a bunch of other licenses of interest to the community. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The library will produce licensing information based on the specifications of calling libraries and programs. In addition to generating text for specific licenses, it will also allow an application to enumerate which licenses are currently available and provide descriptive text for each license, and for license features. It should also provide an easy way to specify "verify at" URLs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The benefit of this library is that applications linking to it can correctly offer licensing choices, and these choices can be transparently updated through package managers as license versions are updated. Human readable descriptions will also be internationalized, preferably using the same .po files used by the CC web site. Hence liblicense will take advantage of package updating and i18n systems to allow applications to always provide c | ||
| + | current and correct licensing choices and license text. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Part of the project is also to provide wrappers for the library for other languages, and to help external developers add metadata support to their projects. A good start will probably be to wrap the library for Python, and use it for ccpublisher. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We will also integrate a module system so that libraries can be used to embed and extract metadata in/from common formats. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As liblicense itself deals only with text strings, we can also make GUI libraries to provide dialogs which present these strings to the user in desktop or web applications. This layering ensures that such dialogs present consistent licensing choices. | ||
== System Overview == | == System Overview == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 35: | ||
[[Image:System_architecture.svg | svg version]] | [[Image:System_architecture.svg | svg version]] | ||
| − | == Config Modules == | + | === Implementation === |
| + | This library will be implemented in C to provide maximum portability. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Interface === | ||
| + | * get_jurisdiction(uri) - ''returns the jurisdiction for the given license.'' | ||
| + | * get_jurisdictions(short or bitcode) - ''returns the available jurisdiction for the given short name or bitcode.'' | ||
| + | * get_locale(uri) – ''returns the locale for the given license.'' | ||
| + | * get_locales(jurisdiction, short or bitcode) – ''returns the available locales for the given jurisdiction and short name or bitcode.'' | ||
| + | * get_name(uri) – ''returns the name of the license.'' | ||
| + | * get_version(uri) – ''returns the version of the license.'' | ||
| + | * get_versions(short, jurisdiction) - ''returns the available versions for the given short name or bitcode and jurisdiction.'' | ||
| + | * get_short(uri) - ''returns the short name for the given uri.'' | ||
| + | * has_flag(attribute,uri) – ''returns if the flag is set for the given uri.'' | ||
| + | * family_flags(family) - ''returns the flags available for a given family.'' | ||
| + | * family(uri) – ''returns the family the given uri belongs to.'' | ||
| + | * get_notification(uri[,url]) - ''returns the notification string for the given url with an option to provide a verification url.'' | ||
| + | * verify_uri(uri) - ''returns whether or not the given uri is recognized by the system.'' | ||
| + | * get_license(family,flags, jurisdiction,locale) – ''returns the uri which satisfies the given attributes.'' | ||
| + | * get_all_licenses() - ''returns a null-terminated list of all general licenses available.'' | ||
| + | * get_general_licenses(family) - ''returns a null-terminated list of all general licenses in a family.'' | ||
| + | * get_families() – ''returns a null-terminated list of available families.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Data Structure === | ||
| + | * Data Types (informal) | ||
| + | ** uri | ||
| + | ** name | ||
| + | ** notification | ||
| + | ** deed | ||
| + | ** sampling | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Config Modules === | ||
* '''in_use'''() - returns whether or not the corresponding config system exists on the computer | * '''in_use'''() - returns whether or not the corresponding config system exists on the computer | ||
* '''get'''() - returns the current default license uri | * '''get'''() - returns the current default license uri | ||
* '''set'''(uri) - sets the default license uri and returns 0 upon success (non-zero for errors) | * '''set'''(uri) - sets the default license uri and returns 0 upon success (non-zero for errors) | ||
| − | == I/O Modules == | + | === I/O Modules === |
* '''mime_types''' - null terminated list of handled mime-types (all indicates external storage method which works for any file) | * '''mime_types''' - null terminated list of handled mime-types (all indicates external storage method which works for any file) | ||
* '''read'''(filename) - returns the license uri for the given file (embedded license takes precedence) | * '''read'''(filename) - returns the license uri for the given file (embedded license takes precedence) | ||
* '''write'''(filename,uri) - writes the license uri for the given file | * '''write'''(filename,uri) - writes the license uri for the given file | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Bindings === | ||
| + | *Python | ||
== License Files (.rdf) == | == License Files (.rdf) == | ||
| Line 143: | Line 193: | ||
== Frontends == | == Frontends == | ||
| + | |||
See [[Desktop Integration]] | See [[Desktop Integration]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Gnome Summit Discussion === | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the Gnome Summit we explored adding CC licensing to various Gnome applications. Application developers appeared to have a few needs: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * They want to display the appropriate icon (or other) for a particular license. For instance, AbiWord could display a small icon representing license status in the tool bar. Music players could display the icon in the controls area. A music streaming app might want to play a 5 second "Now entering the Creative Commons" chime (much like radio station identification, but for licenses). | ||
| + | * They want to allow the user to easily select a license. This would probably be a wizard that asks the user questions and tries to select the most appropriate license from all that it knows about. Much like a file selection dialog, but navigating licenses instead of your file system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A low-level liblicense could handle XML parsing required. It would allow the client to determine the questions that need to be asked to select a license, and to download any icons, blurbs, etc for all known license types. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The low-level library solves the first problem above, but not the second. It's still too difficult to ask the user to select a license. Layered on top of the low-level library would be any number of high level libraries that would convert the textual questions into GUI widgets and present them using the appropriate toolkit (GTK+ / KDE / Cocoa / Win32 / etc). This way, adding license awareness to an application should be as easy as "license=SFGetLicense(); saveDocument(license)". | ||
== Timeline == | == Timeline == | ||
Revision as of 01:00, 23 June 2007
A library for managing license metadata, in particular CC licensing information.
The idea of this library started out on the IRC channel, in a discussion on how to best help boost the community of software developers working with things related to CC - mostly the metadata format.
Basically, the idea is to write a portable C library that manages metadata for CC licenses, and a bunch of other licenses of interest to the community.
The library will produce licensing information based on the specifications of calling libraries and programs. In addition to generating text for specific licenses, it will also allow an application to enumerate which licenses are currently available and provide descriptive text for each license, and for license features. It should also provide an easy way to specify "verify at" URLs.
The benefit of this library is that applications linking to it can correctly offer licensing choices, and these choices can be transparently updated through package managers as license versions are updated. Human readable descriptions will also be internationalized, preferably using the same .po files used by the CC web site. Hence liblicense will take advantage of package updating and i18n systems to allow applications to always provide c current and correct licensing choices and license text.
Part of the project is also to provide wrappers for the library for other languages, and to help external developers add metadata support to their projects. A good start will probably be to wrap the library for Python, and use it for ccpublisher.
We will also integrate a module system so that libraries can be used to embed and extract metadata in/from common formats.
As liblicense itself deals only with text strings, we can also make GUI libraries to provide dialogs which present these strings to the user in desktop or web applications. This layering ensures that such dialogs present consistent licensing choices.
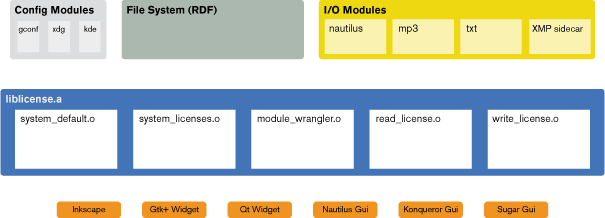
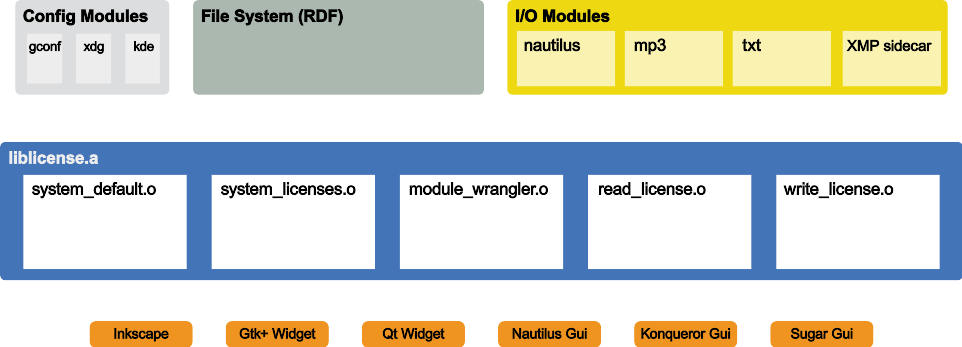
System Overview
Purpose
To provide a simple way for developers to make their applications license aware. Additionally, supplemental modules aim to provide a method for users to track licenses of files on their system. This project complements Companion File metadata specification and Tracker CC Indexing.
Architecture
Implementation
This library will be implemented in C to provide maximum portability.
Interface
- get_jurisdiction(uri) - returns the jurisdiction for the given license.
- get_jurisdictions(short or bitcode) - returns the available jurisdiction for the given short name or bitcode.
- get_locale(uri) – returns the locale for the given license.
- get_locales(jurisdiction, short or bitcode) – returns the available locales for the given jurisdiction and short name or bitcode.
- get_name(uri) – returns the name of the license.
- get_version(uri) – returns the version of the license.
- get_versions(short, jurisdiction) - returns the available versions for the given short name or bitcode and jurisdiction.
- get_short(uri) - returns the short name for the given uri.
- has_flag(attribute,uri) – returns if the flag is set for the given uri.
- family_flags(family) - returns the flags available for a given family.
- family(uri) – returns the family the given uri belongs to.
- get_notification(uri[,url]) - returns the notification string for the given url with an option to provide a verification url.
- verify_uri(uri) - returns whether or not the given uri is recognized by the system.
- get_license(family,flags, jurisdiction,locale) – returns the uri which satisfies the given attributes.
- get_all_licenses() - returns a null-terminated list of all general licenses available.
- get_general_licenses(family) - returns a null-terminated list of all general licenses in a family.
- get_families() – returns a null-terminated list of available families.
Data Structure
- Data Types (informal)
- uri
- name
- notification
- deed
- sampling
Config Modules
- in_use() - returns whether or not the corresponding config system exists on the computer
- get() - returns the current default license uri
- set(uri) - sets the default license uri and returns 0 upon success (non-zero for errors)
I/O Modules
- mime_types - null terminated list of handled mime-types (all indicates external storage method which works for any file)
- read(filename) - returns the license uri for the given file (embedded license takes precedence)
- write(filename,uri) - writes the license uri for the given file
Bindings
- Python
License Files (.rdf)
Attributes
- cc:license
- about
- permits
- requires
- prohibits
- dc:title - The human readable name of the license.
- dc:description - Description of the license.
- dc:coverage - The jurisdiction of the license. (country code from ISO3166)
- dc:language - The language of the license. (language code under RFC3066)
- dc:relation
- dc:type - always "License"
- dc:creator
- dc:publisher
- dc:identifier - URI of license (URI)
Example
<rdf:RDF
xmlns="http://creativecommons.org/ns#"
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
>
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.0/za/">
<dc:title>Creative Commons Attribution No Derivatives</dc:title>
<dc:description>This license allows for redistribution, commercial and non-commercial,
as long as it is passed along unchanged and in whole, with credit to you.</dc:description>
<dc:coverage>
<dcq:ISO3166>
<rdf:value>za</rdf:value>
</dcq:ISO3166>
</dc:coverage>
<dc:language>
<dcq:RFC3066>
<rdf:value>en</rdf:value>
</dcq:RFC3066>
</dc:language>
<dc:hasVersion>2.0</dc:hasVersion>
<dc:isReplacedBy>
<dcq:URI>
<rdf:value>http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.5/za/</rdf:value>
</dcq:URI>
</dc:isReplacedBy>
<dc:isBasedOn>
<dcq:URI>
<rdf:value>http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.5/</rdf:value>
</dcq:URI>
</dc:isBasedOn>
<dc:type>License</dc:type>
<dc:creator>iCommons</dc:creator>
<dc:publisher>Creative Commons</dc:publisher>
<dc:identifier>http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.0/za/</dc:identifier>
<rdf:type rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#License"/>
<permits rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Distribution"/>
<permits rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Reproduction"/>
<requires rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Attribution"/>
<requires rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Notice"/>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
Example (i18n)
<rdf:RDF
xmlns="http://creativecommons.org/ns#"
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
xmlns:dcq="http://purl.org/dc/terms/"
>
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.0/">
<dc:title>
<rdf:Alt>
<rdf:li xml:lang="x-default">Creative Commons Attribution No Derivatives</rdf:li>
<rdf:li xml:lang="es-cl">Creative Commons Atribución-SinDerivadas</rdf:li>
</rdf:Alt>
</dc:title>
<dc:description>
<rdf:Alt>
<rdf:li xml:lang="x-default">This license allows for redistribution, commercial and non-commercial,
as long as it is passed along unchanged and in whole, with credit to you.</rdf:li>
</rdf:Alt>
</dc:description>
<dc:coverage>
<dcq:ISO3166>
<rdf:value>us</rdf:value>
</dcq:ISO3166>
</dc:coverage>
<dc:language>
<dcq:RFC3066>
<rdf:value>en</rdf:value>
</dcq:RFC3066>
</dc:language>
<dc:hasVersion>2.0</dc:hasVersion>
<dc:isReplacedBy>
<dcq:URI>
<rdf:value>http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.5/</rdf:value>
</dcq:URI>
</dc:isReplacedBy>
<dc:type>License</dc:type>
<dc:creator>Creative Commons</dc:creator>
<dc:publisher>Creative Commons</dc:publisher>
<dc:identifier>http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/2.0/</dc:identifier>
<rdf:type rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#License"/>
<permits rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Distribution"/>
<permits rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Reproduction"/>
<requires rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Attribution"/>
<requires rdf:resource="http://creativecommons.org/ns#Notice"/>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
Frontends
Gnome Summit Discussion
At the Gnome Summit we explored adding CC licensing to various Gnome applications. Application developers appeared to have a few needs:
- They want to display the appropriate icon (or other) for a particular license. For instance, AbiWord could display a small icon representing license status in the tool bar. Music players could display the icon in the controls area. A music streaming app might want to play a 5 second "Now entering the Creative Commons" chime (much like radio station identification, but for licenses).
- They want to allow the user to easily select a license. This would probably be a wizard that asks the user questions and tries to select the most appropriate license from all that it knows about. Much like a file selection dialog, but navigating licenses instead of your file system.
A low-level liblicense could handle XML parsing required. It would allow the client to determine the questions that need to be asked to select a license, and to download any icons, blurbs, etc for all known license types.
The low-level library solves the first problem above, but not the second. It's still too difficult to ask the user to select a license. Layered on top of the low-level library would be any number of high level libraries that would convert the textual questions into GUI widgets and present them using the appropriate toolkit (GTK+ / KDE / Cocoa / Win32 / etc). This way, adding license awareness to an application should be as easy as "license=SFGetLicense(); saveDocument(license)".
Timeline
6/18
- Finalize liblicense API.
6/25
- Write liblicense.
- Stub config and IO modules.
7/2
- liblicense python bindings.
7/9
- Gconf config module.
- Nautilus IO module.
7/16
- Nautilus GUI frontend.
- Gnome control panel frontend.
7/23
- Sugar Journal backend.
- Sugar frontend.
7/30
- Bug hunting.
- Frontend polishing.